What to Include in Your WHS Audit: A Guide for Employers
Put simply, a WHS audit is an assessment an organisation’s WHS performance. The audit can be conducted against:
- WHS legislation (WHS Act, Regulations and Code of Practice)
- Internal requirements:
- Internal WHS Management Systems
- Internal policies or procedures
- External standards:
A WHS audit shouldn’t only be a one-time check but rather a continuous process throughout your company’s operations.
It can be quite overwhelming trying to conduct it on your own. Here are some pointers on what should be included in a WHS audit in Australia:
WHS Audit Objectives
The WHS audit is a snapshot in time of how well safety is being managed and crucially identifies where deficiencies exist so they can be addressed. It can be done for a specific project (such as the construction of a new building), or it can be done as part of a company’s overall health and safety management.
 A WHS Audit can have the following objectives:
A WHS Audit can have the following objectives:
- Ensure Compliance with Legislation: Verify that the organization adheres to relevant WHS laws and regulations.
- Example: Checking if safety signage meets the standards set by local WHS regulations.
- Identify Hazards and Risks: Detect potential hazards and assess the risks associated with them.
- Example: Inspecting machinery for proper guarding to prevent accidents.
- Evaluate Effectiveness of Safety Procedures: Assess how well current safety procedures are implemented and followed.
- Example: Reviewing incident reports to see if emergency response procedures were effectively executed.
- Promote a Safety Culture: Foster a culture of safety within the organization.
- Example: Conducting regular safety meetings and encouraging employees to report unsafe conditions.
- Monitor Compliance with Internal Policies: Confirm that internal WHS policies and procedures are being followed.
- Example: Auditing the use of safety checklists during routine inspections.
- Identify Opportunities for Continuous Improvement: Highlight areas where ongoing improvements can be made.
- Example: Suggesting the adoption of new safety technologies or practices to reduce risks.
Depending on the type of work, the WHS audit will usually involve a full or partial inspection of the work area and a review of the worker’s health and safety policies, procedures, or other relevant safety paperwork. The level of detail will depend on the type of work being done and the potential hazards.
Who Should Conduct a WHS Audit?
To be effective and ensure effective consultation, there should be collaboration and communication between relevant stakeholders. The team will usually only consist of a few individuals; however, it may involve more people depending on the scope and objectives. Ideally, the following stakeholders should be involved and consulted:
- The owner of the company or their representative
- The workers involved in the work or their health and safety representative
- The managers and supervisors of the workers in the work area
- The safety officer or safety manager of the company
Many RTOs offer courses on how to become a WHS auditor, for example Global Mark – Lead Auditor Course.
What is a WHS Audit Checklist?
WHS audit checklists are vital for to ensure the auditing process is systematic and comprehensive. A checklist will help you keep track of what areas of your business you need to check, as well as forming the basis of the audit report and record keeping.
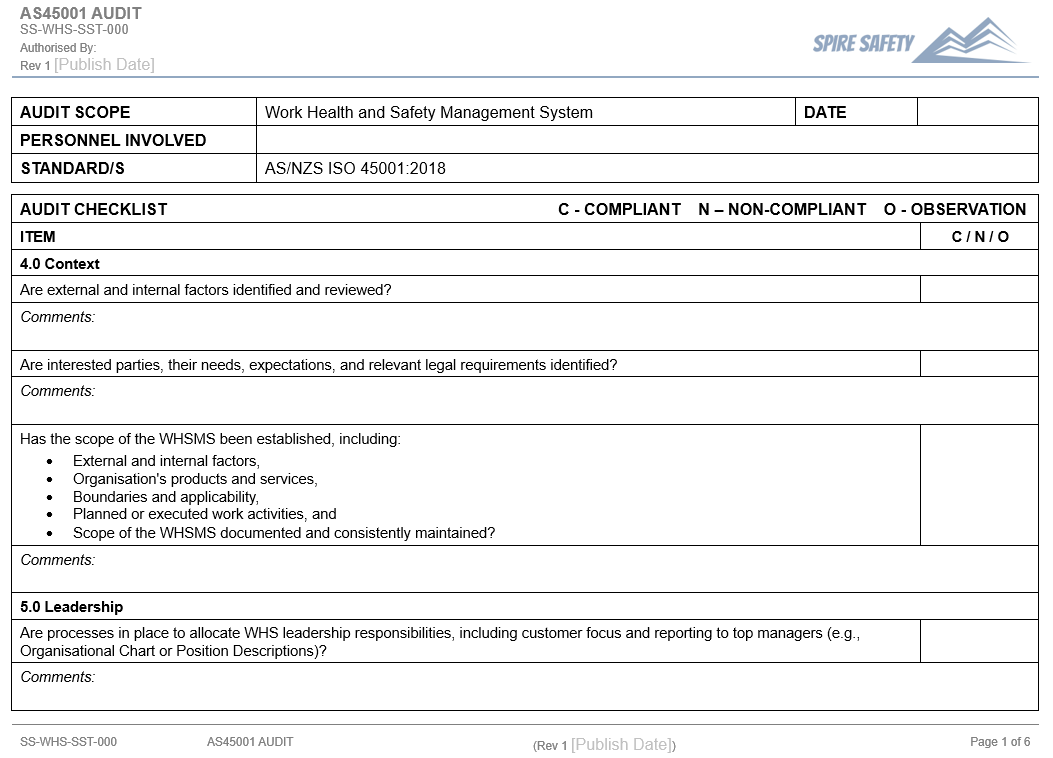
Generally, a WHS audit checklist could include:
- The date, work area/s, methodology and scope of the audit
- Who is part of the auditing team (WHS auditors)
- A list of the checks that are being conducted, for example:
- Is PPE being worn
- Are relevant risk controls in place
- Are safety procedures documented, available, and being followed
- Are workers engaging in unsafe behaviors
- Are adequate housekeeping procedures in place
- Are permit systems in use
- Are first aid and emergency equipment available and fit for use
- Recommended actions / comments
- Date for close-out of recommended actions
You can create your own checklist depending on the type of work being done, or you can use a checklist provided by a regulatory agency. For example, WHSQ provides an internal audit checklist.
FAQs
How often should a WHS Audit be conducted?
The frequency depends on a variety of factors, such as the size and nature of operations and any regulatory requirements. In general, it is recommended that WHS audits be conducted at least once per year
Why are WHS audits important?
WHS audits help identify potential hazards, ensure compliance with safety regulations, and promote continuous improvement in safety performance. They are essential for preventing accidents and injuries in the workplace.
What is involved in a WHS audit?
A WHS audit typically involves reviewing documentation, interviewing employees, and observing workplace conditions. The auditor assesses compliance with safety policies, identifies hazards, and recommends corrective actions.
How can we prepare for an audit?
Preparation for an audit includes:
- Reviewing and updating safety policies and procedures.
- Ensuring all safety records and documentation are complete and accessible.
- Conducting internal inspections to identify and address potential issues before the audit.
Did You Know?
The landmark case of Thistle Co of Australia Pty Ltd v Bretz (2018) highlighted the critical importance of safety audits in the workplace. In this case, the Queensland Court of Appeal found that the company had failed to conduct adequate safety audits, which contributed to an employee’s injury. The court emphasized that regular and thorough safety audits are essential for identifying and mitigating risks, thereby preventing workplace accidents1.
Articles and Further Reading
- WHS Compliance Auditing (Spire Safety) <https://spiresafety.com.au/services/safety-consultancy/whs-audits/>
- Audits and inspections (WHSQ) <https://www.worksafe.qld.gov.au/laws-and-compliance/compliance-and-enforcement/audits-and-inspections>
