Leadership Commitment’s Affect On WHS
WHS leadership commitment is essential to a work health and safety management system because it sets the tone for the organization and demonstrates the importance placed on the health and safety of employees.
What is Leadership Commitment?
Leadership commitment means that leaders (e.g. owners and managers) should prioritize and actively promote a safe and healthy workplace environment.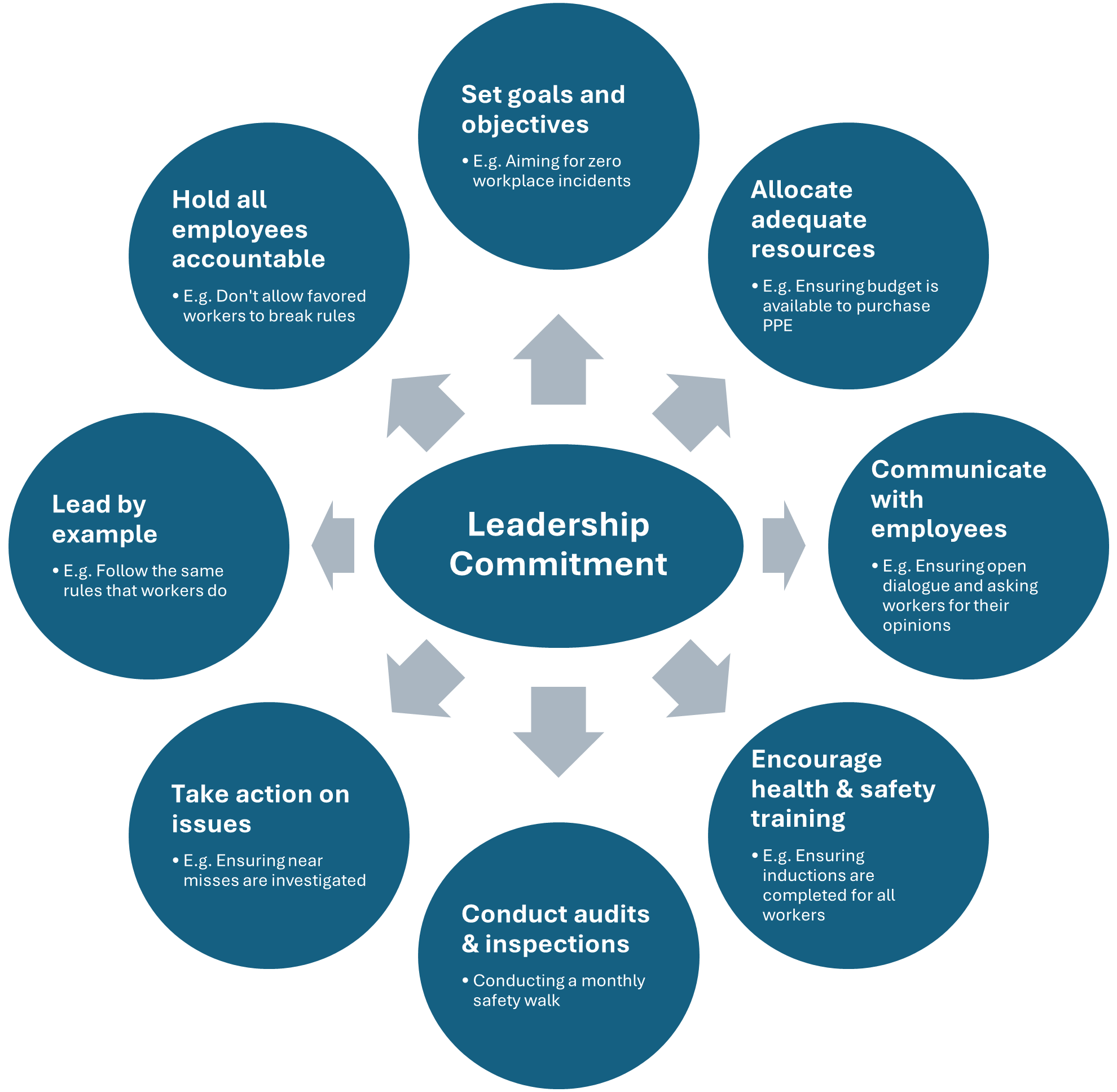 WHS leadership commitment can be demonstrated in several ways, including:
WHS leadership commitment can be demonstrated in several ways, including:
- Setting goals and objectives: E.g. Aiming to achieve zero serious workplace incidents.
- Allocating adequate resources (e.g. time and money): E.g. Ensuring budget is available to purchase PPE.
- Communicating with employees about health and safety: E.g. Ensuring open dialogue and asking workers for their opinions.
- Encouraging health and safety training: E.g. Ensuring health and safety inductions are completed for all workers.
- Conducting safety audits and inspections: Conducting a monthly safety walk.
- Taking prompt action on WHS issues: E.g. Ensuring near misses are investigated.
- Leading by example: E.g. Follow the same rules that workers are expected to follow.
- Holding all employees accountable: E.g. Don’t allow favored workers to break rules.
By demonstrating a strong WHS leadership commitment to work health and safety, leaders can create a culture in which all employees feel responsible for maintaining a safe work environment and are motivated to work safely.
Why a WHS Policy is Important
A WHS Policy clearly outlines the organization’s commitment to work health and safety.
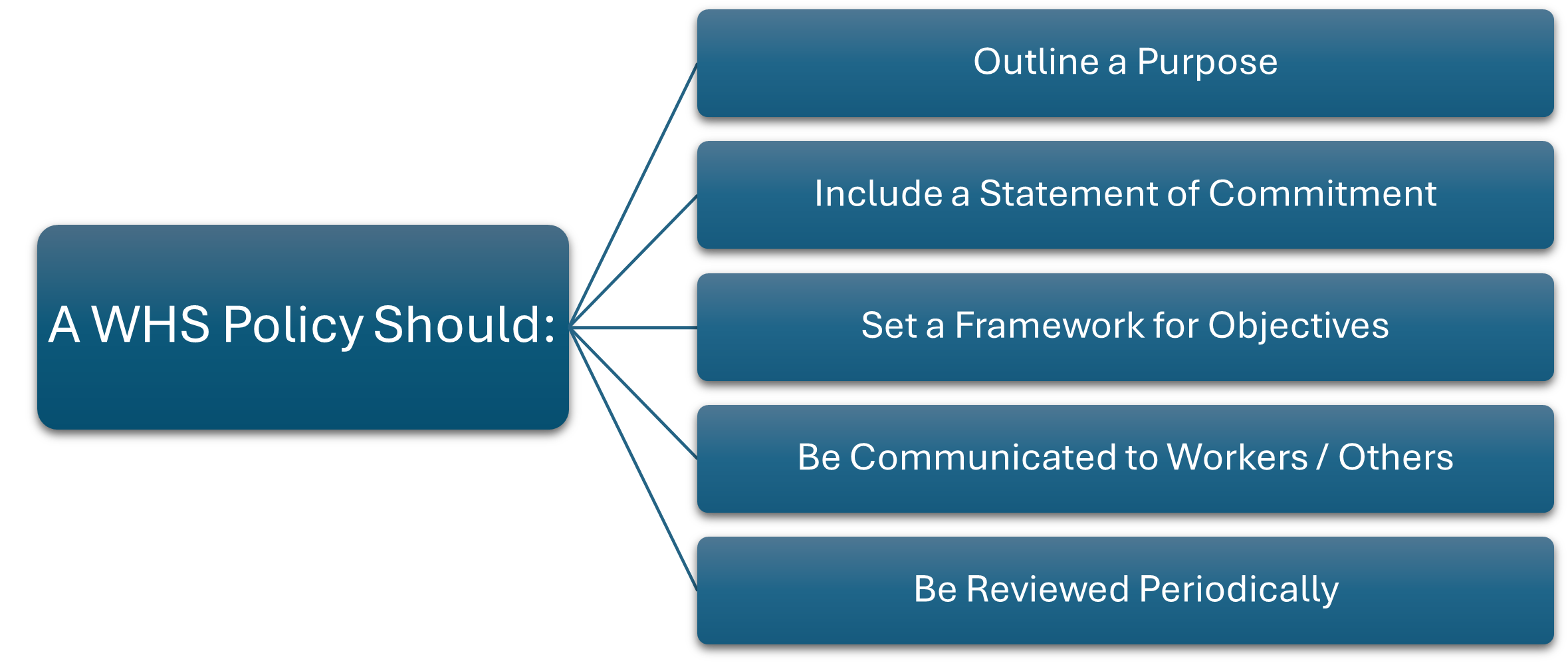 Some key elements that should be included in a WHS leadership commitment policy are:
Some key elements that should be included in a WHS leadership commitment policy are:
- Purpose: A clear statement of the purpose of the policy and the organization’s commitment to work health and safety.
- Responsibilities: A clear definition of the responsibilities of leadership and employees in relation to work health and safety, and how they will work together to maintain a safe work environment.
- Allocation of Resources: A commitment to allocate the necessary resources, including personnel, funding, and technology, to support the work health and safety management system.
- Communication: A commitment to communicate regularly and openly with employees about health and safety issues and to promote a culture of safety throughout the organization.
- Training: A commitment to provide health and safety training to all employees and to ensure that they have the knowledge and skills they need to work safely.
Inspection and Audit: A commitment to conduct regular safety inspections and audits and to take prompt action to address any identified hazards or safety concerns. - Review and Evaluation: A commitment to regularly review and evaluate the work health and safety management system to ensure that it remains effective and to identify areas for improvement.
By including these key elements, a WHS leadership commitment policy can provide clear guidance and expectations for all employees and help to establish a culture of safety in the organization.
The Cost of Poor WHS Leadership
Poor WHS leadership commitment can lead to increased accident rates, higher employee turnover, low morale, and legal penalties. Additionally, it can damage the organization’s reputation, increase absenteeism, and result in higher costs.
Building a Safety Culture
Safe Work Australia’s guide to “Promoting effective health and safety leadership” outlines the following examples of an effective safety culture:
- An informed culture where those who manage and operate the system have current knowledge about the human, technical, organisational and environmental factors that determine the safety of the system as a whole.
- A reporting culture in which people are willing to report errors and near misses.
- A just culture with a culture of ‘no blame’ where an atmosphere of trust is present and people are encouraged or even rewarded for providing essential safety-related information—but where there is also a clear line between acceptable and unacceptable behaviour.
- A flexible culture characterised as shifting from the conventional hierarchical mode to a flatter professional structure.
- A learning culture in which there is the willingness and the competence to draw the right conclusions from its safety information system, and the will to implement major reforms when the need is indicated..
FAQs
What is WHS leadership commitment?
WHS leadership commitment is the dedication of leaders to prioritize and promote workplace health and safety.
Why is WHS leadership commitment important?
It ensures a safe working environment and reduces the risk of accidents and injuries.
How can leaders demonstrate WHS commitment?
By actively participating in safety programs and setting a positive example.
What role do leaders play in WHS?
Leaders are responsible for creating and maintaining a culture of safety.
How does WHS leadership commitment benefit employees?
It fosters a safer, healthier, and more productive workplace.
What are some key actions for WHS leadership?
Regular safety training, clear communication, and continuous improvement.
Did You Know
Did you know that the origins of modern Work Health and Safety (WHS) leadership commitment can be traced back to the Industrial Revolution? During this period, pioneering leaders like Robert Owen, a Welsh social reformer, advocated for safer working conditions and shorter work hours, laying the groundwork for today’s WHS standards. Owen’s commitment to worker welfare not only improved safety but also demonstrated that prioritizing employee health could lead to increased productivity and loyalty, a principle that continues to influence WHS leadership today.
Articles and Further Reading
- What is a WHSMS (Work Health and Safety Management System)? (Spire Safety) <https://spiresafety.com.au/resources/what-is-a-whsms/>
- Promoting effective health and safety leadership (Safe Work Australia) <https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/system/files/documents/1702/promoting-effective-health-safety-leadership-march-2011-barry-sherriff.docx>
- Leadership and culture (Safe Work Australia) <https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/safety-topic/managing-health-and-safety/leadership-and-culture>
