Mastering WHS Training Programs in Australia: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of workplace safety, implementing effective WHS training programs is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Work Health and Safety (WHS) training in Australia.
From understanding the basics to mastering industry-specific nuances, this guide is your go-to resource for creating impactful training programs.
Key Takeaways:
- WHS (Work Health and Safety) refers to laws and regulations in Australia aimed at protecting workers from risks, hazards, injuries, and illnesses in the workplace.
- The Australian WHS Strategy 2023-2033 focuses on reducing work-related fatalities, injuries, and illnesses through four key objectives.
- Effective WHS training involves a thorough needs assessment, appropriate training methods, engaging content creation, and compliance tracking.
WHS Training Programs: A Deep Dive
Understanding WHS Basics
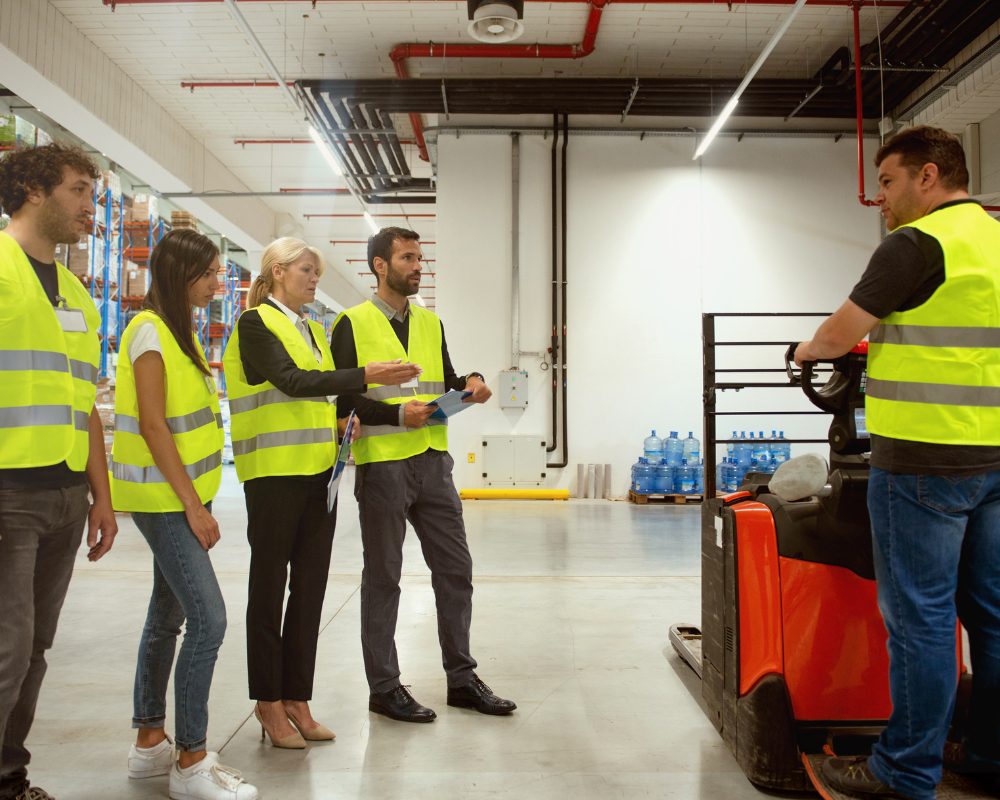
Work Health and Safety (WHS) laws and regulations in Australia are designed to promote health, safety, and welfare in the workplace. Employers play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance and safeguarding their workforce.
The Australian WHS Strategy 2023-2033
The new 10-year strategy by Safe Work Australia aims to prioritize health and safety in all aspects of work design, strengthen safety culture, ensure responsive regulatory frameworks, and use research to inform policies and identify risks.
Read more about the Australian WHS Strategy 2023-2033
Best Practices for WHS Training
Implementing WHS training programs involves several best practices, including:
- Conducting a thorough training needs assessment.
- Selecting appropriate training methods, such as online courses.
- Developing structured programs with clear goals and objectives.
- Creating engaging learning content.
- Tracking training results and ensuring compliance through record-keeping.
Industry-Specific WHS Training
Certain sectors, like construction and mining, are considered higher risk and require specialized safety training. Employers in these industries must go beyond general WHS training to address specific hazards and risks associated with their operations.
Online WHS Training: Benefits and Considerations
Online WHS training offers flexibility, cost reduction, and detailed record-keeping for auditing purposes. Employers should leverage these advantages while ensuring the effectiveness of online training programs.
Implementing WHS Training: Step-by-Step Guide
- Assessing Needs: Conduct a thorough analysis of your workplace’s specific requirements.
- Choosing a Method: Select the most suitable training method, considering factors like industry, workforce size, and training objectives.
- Creating a Program: Develop a structured training program with clear goals and objectives.
- Developing Content: Create engaging and informative learning materials, possibly with the help of Subject Matter Experts (SMEs).
- Delivering the Training: Execute the training program using suitable platforms or Learning Management Systems (LMS).
- Measuring Outcomes: Regularly assess the effectiveness of the training, ensuring compliance and continuous improvement.
FAQ
Q: What is WHS?
A: WHS stands for Work Health and Safety, encompassing laws and regulations in Australia aimed at protecting workers from workplace risks and hazards.
Q: Why is industry-specific WHS training important?
A: Industries like construction and mining have unique risks, requiring specialized training to address sector-specific hazards effectively.
Advice & Actionable Tips
For employers looking to enhance their WHS training programs:
- Regularly review and update training materials based on industry changes.
- Encourage worker participation in safety initiatives.
- Address psychosocial hazards alongside physical risks.
- Provide ongoing training and reviews to ensure a continuously improving WHS process.
Conclusion
Mastering WHS training programs is a continuous journey towards creating safer workplaces.
By understanding the intricacies of WHS laws, implementing best practices, and staying informed about industry-specific requirements, employers can foster a culture of safety, reduce incidents, and ensure the well-being of their workforce.