What is a Confined Space? Everything You Need to Know
What is a Confined Space?
Read our article to determine what is legally considered a confined space. Download our Confined Space Identification Checklist to assess spaces in your workplace.
*For internal use only. Not for resale or redistribution. By downloading any content from this article, you agree to our Free Resources Licensing Agreement.
NOTE: This document is a template only and it must be customised for your business. Other aspects that may need to be considered include, but are not limited to, ensuring that:
- Relevant legal requirements have been met,
- Workplace specific risks are identified and managed, and
- Workers are consulted with during the customisation / review process.
Who Decides What is a Confined Space?
In Australia, each state has the authority to set work health and safety laws. To ensure you are using the correct legislation, you should access it from your jurisdictions local regulator.
The Harmonised WHS Legislation and Codes
Most of Australia uses the Harmonised WHS Legislation and that is the legislation we’ll be referencing today. This model legislation is published by Safe Work Australia and is comprised of the Work Health and Safety Act and Regulations.
Safe Work Australia also published model codes of practice. There is a model code of practice for confined space that has been adopted in most states. Once again, we’ll be referencing the harmonised confined spaces code of practice.
A Definition for Confined Spaces
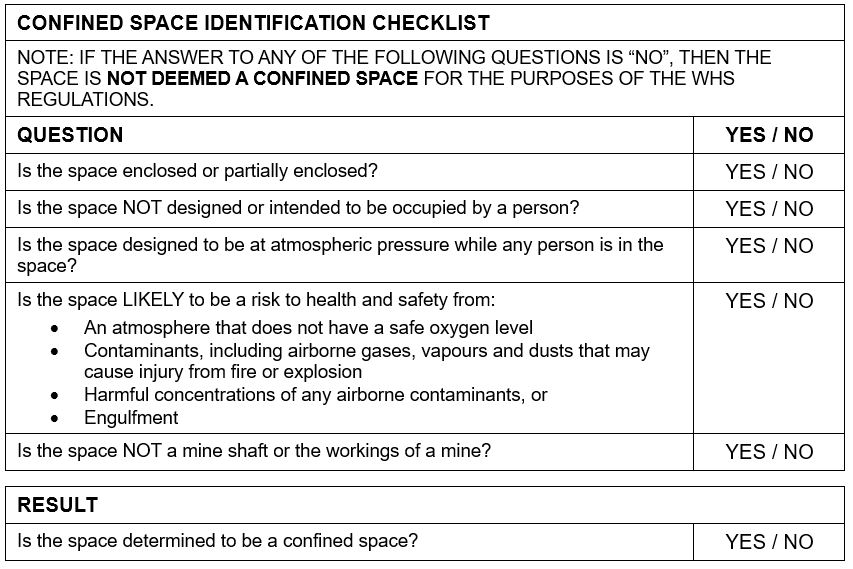
The confined spaces code of practice contains a flowchart that is used to assess whether a space meets the criteria. Most of the questions are straight forward, however some can be tricky and even subjective. If you answer NO to any of the following questions, the space is NOT considered a confined space.
Enclosed or Partially Enclosed?
Pretty straight forward. If the space isn’t enclosed (e.g. you are standing in the middle of a field) this obviously isn’t a confined space.
NOT Designed to Be Occupied by a Person?
Next question – is the space designed for human occupancy? Example – your car is an enclosed space, but it is designed for a person to be inside, therefore it is NOT considered a confined space. Your house is another example, it is designed with ventilation, lighting, safe access and egress etc. so it also NOT a confined space.
The tricky thing here is the question is a “double negative”. If the space IS designed for a person to be inside, the answer to the question is NO.
Designed to Be at Normal Atmospheric Pressure?
This is the question that confuses most people. Take the example of a high pressure vessel that isn’t at atmospheric pressure. The answer to this question is obviously NO. However that doesn’t mean that this space isn’t a confined space and that people can enter it without permit. Rather, it means that the space is highly dangerous and people must not enter it. Before it can be considered a confined space, it must be brought to atmospheric pressure.
LIKELY to Pose Health and Safety Risks?
This is the subjective question. After all, how do you quantify “likely”? The risks that may be present are:
- Unsafe or low oxygen levels
- Contaminants that may cause ignition or fire, including:
- Gases
- Vapors
- Dusts
- Harmful concentration of airborne contaminants (e.g. toxic gases or toxic fumes)
- Engulfment
This question is best answered by a competent person conducting a written risk assessment in consultation with workers.
NOT a mine shaft or the workings of a mine?
Another double negative question. If the answer is NO, i.e. the space IS a mine shaft or mine, then the space is NOT a confined space. In this case, the space will be regulated by the mining regulator in your jurisdiction.
Examples of Confined Spaces
Lets run through those questions for two examples.
Underground Sewers / Manhole
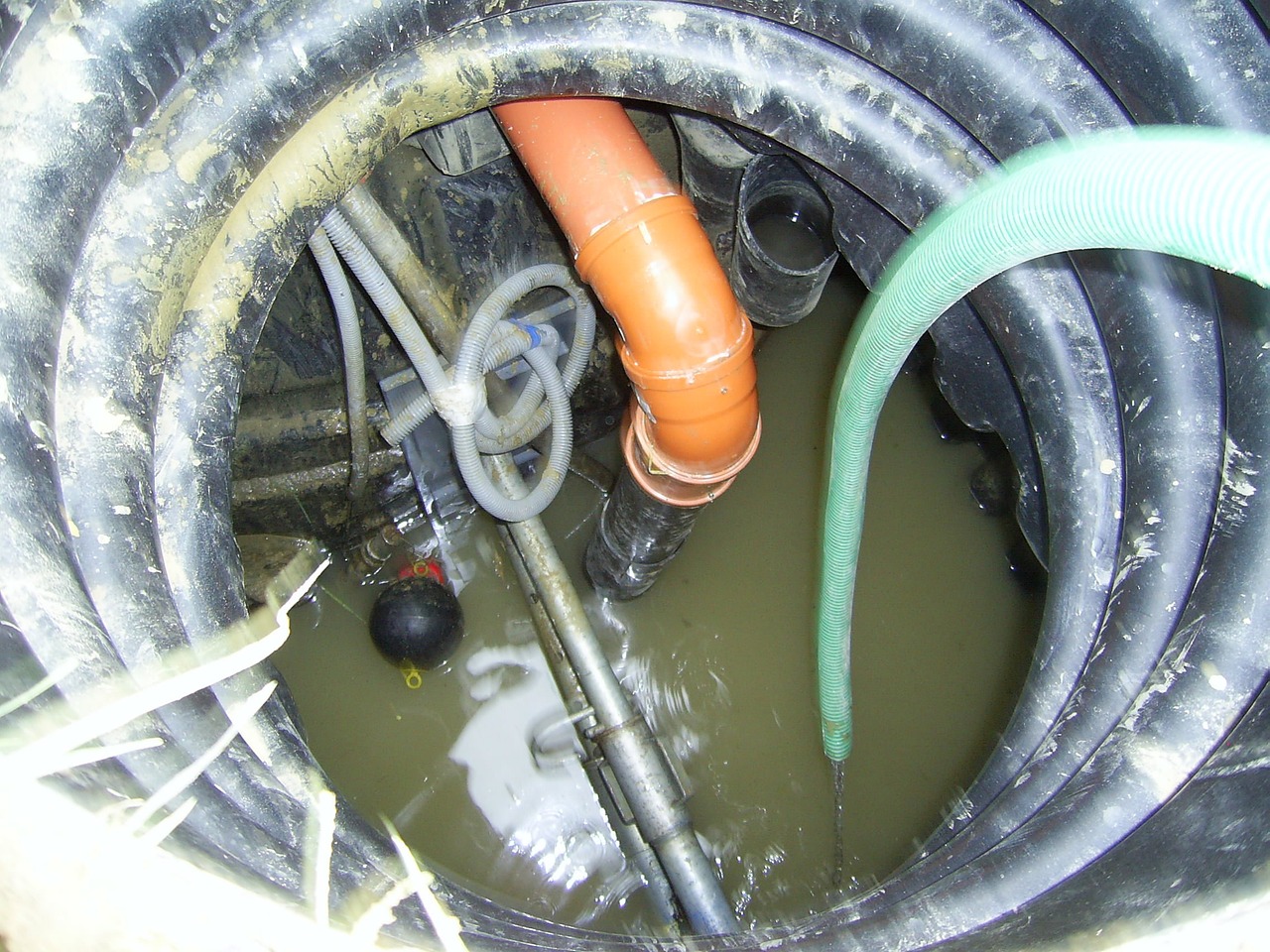

- Is the space enclosed or partially enclosed? Yes.
- Is the space NOT designed for a person to be inside? Yes.
- Is the space at atmospheric pressure? Yes.
- Is the space likely to pose health and safety risks? Yes.
- Is the space NOT a mine shaft or mine? Yes.
Therefore the space is a confined space.
New, Clean Storage Tanks (not connected)

- Is the space enclosed or partially enclosed? Yes.
- Is the space NOT designed for a person to be inside? Yes.
- Is the space at atmospheric pressure? Yes.
- Is the space likely to pose health and safety risks? No (answer taken from the code).
- Is the space NOT a mine shaft or mine? Yes.
Therefore the space is NOT a confined space.
Some examples of what would likely be a confined space include silos, chimneys, dry wells, vats, ducts and flues.
Safety Controls for Confined Space Entry
Once it has been determined what is a confined space, various control measures may be required including:
- Confined space entry permit
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) (e.g. respiratory protective equipment and harnesses)
- Purging or forced ventilation
- Atmospheric monitoring
- Isolation of machinery or pipes / valves
- Rescue procedures, first aid and emergency procedures (including means of communication)
- Trained and competent workers
- Safe system of work (SWMS) or safe work practices
Check with your local regulator to determine specific duties in your state.
Confined Spaces Identification Checklist
We have developed a Confined Space Identification Checklist to help identify what is a confined space. For more information, contact one of our friendly consultants.