What is a WHSMS (Work Health and Safety Management System)?
What is a WHSMS?
Work Health and Safety Management Systems (WHSMS) are a set of documents which outline how WHS is managed within an organisation. These documents include a WHSMS Manual, Policies and Procedures.
Need AS/NZS ISO 45001 Certification? Call us now or check out our detailed guide:
WHS Management Systems are designed to identify and control hazards, reduce the likelihood of accidents and incidents, and improve overall safety performance.

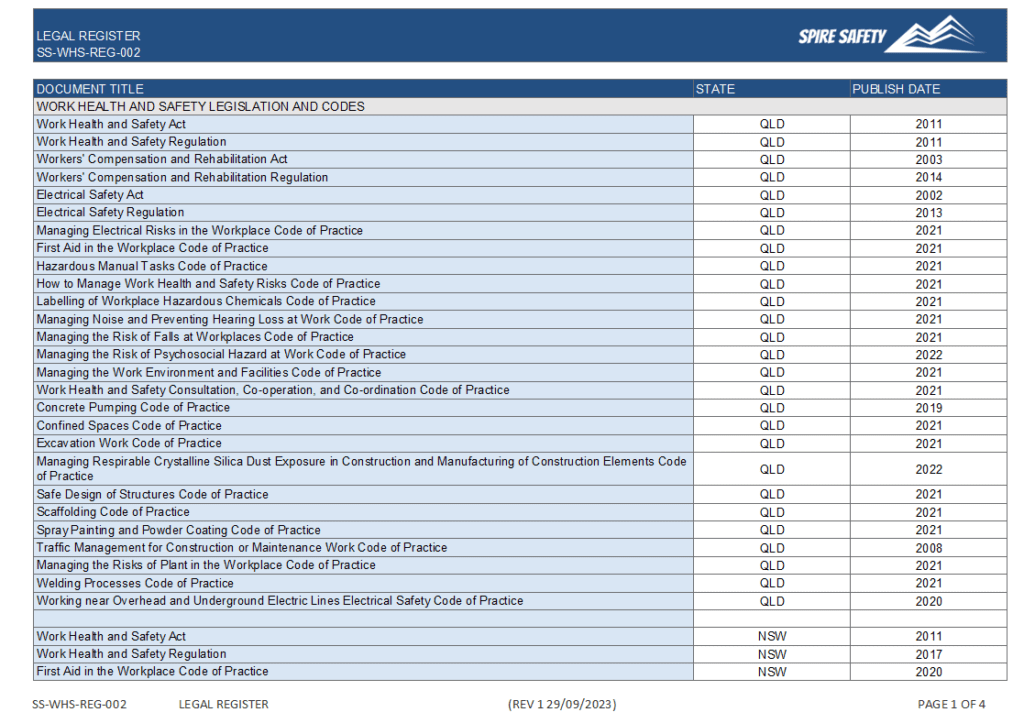
WHS Documentation
A WHS Management System contains documentation which a describe how the organisation ensures the safety of workers. Examples of WHSMS documentation:
- Policies:
- Work Health and Safety
- Drug and Alcohol
- Fitness for Work
- Procedures:
- Risk Management
- Subcontractor Management
- Manual Handling
- Registers:
- Master Document Register
- SDS Register
- Training Register
- Corrective Actions Register
- Form and Tools:
- Inductions
- Safety Inspections
- Safe Work Method Statements
- Safe Operating Procedures
These documents can either be paper-based or cloud-based / digital.
WHS Policies
WHS Policies are usually short, overarching statements that guide an organization’s thinking, attitude, or values towards the management of safety risks.

Policies are often signed by the director and displayed on the office wall or website.
WHS Procedures
WHS procedures are usually longer documents that give step-by-step guidance on how an organization manages safety issues, for example a First Aid Procedure or Risk Management Procedure.

WHS Registers
WHS Registers are usually excel spreadsheets that are used to organise, track or view data. For example, a Master Document Register tracks all the documents within a WHSMS (as well as review dates and approvals).
WHS Forms and Tools
WHS Forms and Tools are the front-end documentation that are used by workers and managers to assist in managing WHS. Examples include WHS Inductions, Inspections or Safe Work Method Statements (SWMS).
What is ISO 45001:2018?
The ISO standard for WHS Management Systems is called ISO 45001:2018 Occupational health and safety management systems. Australia has “adopted” the standard and renamed it AS/NZS 45001:2018. The standard covers:

Implementing a WHS Management System that complies with AS/NZS 45001:2018 demonstrates that your organisation is performing to the highest international standard of WHS.
Benefits of WHS Management Systems
WHS Management Systems protect workers and ensure a safe workplace. According to Safe Work Australia, the total cost of workplace injuries and illnesses in Australia in the 2017-18 financial year was estimated to be $61.8 billion, which represents 4.1% of the country’s GDP. This cost includes both direct and indirect costs, such as:
- Direct costs: Medical expenses, workers’ compensation payments, and the cost of replacing damaged equipment.
- Indirect costs: Lost productivity, absenteeism, and the cost of training replacement workers.
The WHSMS can also help boost a company’s reputation and help win larger contracts. Other reasons to have a WHS Management System include:

Risk Management via a WHSMS
The code of practice “How to manage work health and safety risks” provides risk management requirements for business. In general, WHS risk management has the following 4 steps:

Step 1 – Identify Hazards
Hazards can be identified by
- Consultation with:
- Workers,
- Managers,
- Contractors,
- WHS Inspections,
- Reviewing the WHS Act, Regulations, Codes of Practice or WHS Alerts, and
- Incident Reports and Investigations.
Step 2 – Assess Risks
A risk matrix is used to assess the risk in terms of likelihood and consequence and scored from Low to Catastrophic.

Step 3 – Implement Controls
Controls are ways that we can protect ourselves and others. Controls can be categorised in order of Most Effective to Least Effective (the hierarchy of controls):

Step 4 – Monitor and Review
Controls should be monitored and reviewed to ensure they remain effective. Controls can be monitored and reviewed by:
- Ongoing supervision,
- Consultation with workers,
- WHS inspections,
- Internal audits, and
- Analyzing incident and near-miss reports.
How to Develop a WHSMS
Conduct an assessment of workplace hazards to understand your risks. Review the relevant codes of practice and engage stakeholders, including workers, to develop policies and procedures. Finally implement these measures with effective communication, training, and monitoring processes to ensure continuous improvement.
To build your own WHSMS, check out our free resources:
- Free Policies
- Free Procedures
- Free Forms and Tools
- Free Plant Risk Assessments
- Free Verifications of Competency
Alternatively, to purchase our easy-to-use “off the shelf” WHSMS, contact us.
How Do I Get ISO Certified?
We help organisations get ISO certified. Contact us to learn more.
To become certified to ISO 45001, organizations must go through a certification process that involves an independent assessment of their Work Health and Safety Management Systems by a certified third-party auditor. This assessment is designed to verify that the organization’s WHSMS meets the requirements of the standard.
Once the organization has been certified, they are required to undergo yearly surveillance audits to ensure that they continue to meet the requirements of the standard.
How Can Leaders Demonstrate Commitment?
Leadership start at the top, and so does safety! Leaders can demonstrate commitment by:

WHS leadership is crucial because it sets the safety culture’s tone, demonstrating that health and safety are prioritized at all organizational levels. Strong leadership in WHS can be demonstrated by taking ownership, providing resources and setting objectives.
A Summary of WHSMS
Work health and safety management systems (WHSMS) are a systematic approach to managing safety that aims to:
- Improve legal compliance
- Reduce the likelihood of accidents and incidents
- Continuously improve WHS performance
The WHSMS contains various documents (policies and procedures) to manage WHS in the workplace.
FAQs
What are the legal requirements for a WHSMS?
There is generally no legal requirement to have a documented WHSMS (with some exceptions).
What costs are associated with implementing a WHSMS?
Implementing a WHSMS typically involves the following costs:
- Time / salary
- Purchase of documentation
- Engaging a WHS consultant or manager
- Training and education
What role do workers play in a WHSMS?
Identifying hazards, providing feedback, undergoing training and implementing procedures are all undertaken by workers.
How often should a WHS Management System be reviewed?
Typically, most WHS Management Systems are reviewed at least yearly.
Further Reading
- What is ISO 45001 Certification and How Do I Get Certified? (Spire Safety) <https://spiresafety.com.au/resources/iso-45001-certification/>
- What are the WHS Penalties for Non-Compliance? (Spire Safety) <https://spiresafety.com.au/resources/whs-penalties-for-non-compliance/>
- Work Related Deaths Per Year in Australia: Facts and Figures (Spire Safety) <https://spiresafety.com.au/resources/work-related-deaths-per-year/>
- Workplace health and safety management system (Comcare) <https://www.comcare.gov.au/safe-healthy-work/healthy-workplace/whs-system>
